Hepatitis C Viral RNA, Quantitative, Real-Time PCR Most Popular
- $628.57
- $183.95
- Save: 70.74%
The following is a list of what is included in the item above. Click the test(s) below to view what biomarkers are measured along with an explanation of what the biomarker is measuring.
Also known as: Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative RealTime PCR
HCV RNA, Quantitative
HCV RNA, Quantitative
HCV RNA, Quantitative
HCV RNA, Quantitative
The Hepatitis C Viral RNA, Quantitative, Real-Time PCR test contains 1 test with 4 biomarkers .
Brief Description: The Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) test is a highly sensitive and specific molecular diagnostic test used to detect and quantify the amount of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genetic material (RNA) present in a blood sample. This test is essential for diagnosing and monitoring hepatitis C infection.
Also Known As: HCV Test, HCV RNA Test, HCV Viral Load Test
Collection Method: Blood Draw
Specimen Type: Serum
Test Preparation: No preparation required
When is a Hepatitis C Viral RNA test ordered?
When an antibody test is positive, more testing is required to confirm an active infection, such as an HCV RNA test or viral load. In some labs, if the HCV antibody test is positive, this test will be run immediately.
Testing for HCV viral load may be required before starting therapy, on a regular basis to track treatment response, and at the end of treatment to gauge its efficacy.
What does a Hepatitis C Viral RNA test check for?
The liver infection known as hepatitis C is brought on by a virus and is characterized by liver inflammation and destruction. Hepatitis C tests are a collection of tests used to identify, pinpoint, and track the progress of a hepatitis C virus infection. The most popular HCV test checks for blood antibodies created in response to an HCV infection. Other tests identify the specific subtype of the virus or measure the quantity or presence of viral RNA.
One of the five hepatitis viruses known to cause the disease, along with hepatitis A, B, D, and E, is hepatitis C. HCV is spread through contact with contaminated blood, primarily through the sharing of needles by intravenous drug users, but it can also be transmitted through sex with an infected person, through occupational exposure in the healthcare industry, and, less frequently, from a mother to her unborn child during childbirth. Before HCV testing were made available in the 1990s, blood transfusions were a common way for HCV to spread.
There is presently no vaccination to prevent infection with HCV, despite the fact that it is less contagious than hepatitis B. In North America, hepatitis C infection is a typical contributor to chronic liver disease. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were roughly 30,500 cases of acute hepatitis C in the United States in 2014, and there are between 2.7 and 3.9 million Americans who have chronic hepatitis C.
Many infected people exhibit no symptoms and are unaware of their illness. The acute HCV infection may not manifest any symptoms or only mild, nonspecific ones, whereas the chronic infection may go unnoticed for ten or twenty years before producing enough liver damage to impair liver function.
Hepatitis C antibody tests are used to check for the infection in persons, such as those with risk factors but no visible symptoms, those who have hepatitis or liver disease symptoms, or those who have been exposed to the virus.
A positive antibody test is followed by a hepatitis C RNA test, which detects the genetic material of the virus, because the antibody test can remain positive in the majority of patients even though they have recovered from the infection. A positive RNA test result indicates the virus is present, the infection has not cleared up, and treatment may be necessary.
A liver panel is a collection of tests that doctors might conduct to evaluate the condition of the liver.

Lab tests often ordered with a Hepatitis C Viral RNA test:
When a Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative test is ordered, it's often part of a broader evaluation of liver health and hepatitis C infection management. Here are some tests commonly ordered alongside it:
-
- Purpose: To screen for past or present HCV infection by detecting antibodies to the virus.
- Why Is It Ordered: An initial positive HCV antibody test is typically followed by a Hepatitis C Viral RNA test to confirm active infection, as antibodies may be present from a past infection that has resolved or from a current active infection.
-
- Purpose: To assess liver health.
- Why Is It Ordered: To evaluate the impact of HCV on liver function and to monitor liver health during treatment.
-
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg) and Hepatitis B Core Antibody (Anti-HBc):
- Purpose: To test for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
- Why Is It Ordered: To screen for HBV co-infection, which is important in determining the best approach to HCV treatment and management, as HBV reactivation can occur during or after HCV treatment.
-
- Purpose: To evaluate overall blood health.
- Why Is It Ordered: To assess for signs of anemia or thrombocytopenia, which can occur with chronic liver disease and can be affected by certain HCV treatments.
-
INR (International Normalized Ratio):
- Purpose: To measure blood clotting time.
- Why Is It Ordered: To assess liver function and coagulation status, particularly in individuals with advanced liver disease.
-
- Purpose: To evaluate kidney function.
- Why Is It Ordered: To ensure proper kidney function, especially before starting certain HCV treatments that can affect the kidneys.
-
Genotype Testing for Hepatitis C Virus:
- Purpose: To determine the specific genotype of HCV.
- Why Is It Ordered: To guide treatment decisions, as certain medications are more effective against specific HCV genotypes.
These tests, when ordered alongside a Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test, provide a comprehensive evaluation of hepatitis C infection and its impact on the patient's health. They are crucial for confirming active infection, assessing liver health, determining the best treatment options, and monitoring the response to therapy. The specific combination of tests will depend on the individual’s symptoms, clinical presentation, and medical history.
Conditions where a Hepatitis C Viral RNA test is recommended:
The Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test is primarily used for diagnosing and monitoring hepatitis C infection, an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus.
How does my health care provider use a Hepatitis C Viral RNA test?
Hepatitis C tests are used to detect and identify the presence of the hepatitis C virus, to direct therapy, and/or to track the progress of an HCV infection.
The HCV RNA test finds and counts the amount of viral RNA in the blood. This examination may be used to identify an ongoing infection and confirm the virus's existence. By comparing the amount of virus before and after treatment, viral load tests are also used to assist measure the effectiveness of the medication.
What do my Hepatitis C Viral RNA test results mean?
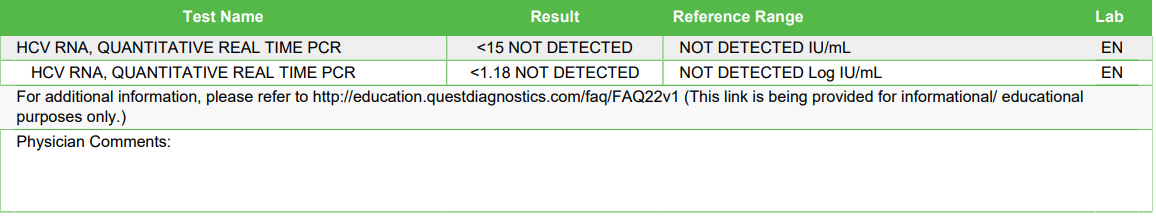
If the virus is present, the HCV viral load test results are given as a number. The result is frequently labeled "negative" or "not detected" if there is no virus present or if the virus concentration is too low to detect it.
The individual has an active infection if the HCV RNA test is positive. If no HCV viral RNA is found, either the person does not have an active infection or there are extremely few copies of the virus in their system.
An HCV viral load can show whether or not treatment is working for monitoring purposes. A high or rising viral load can indicate that the treatment is ineffective, whereas a low, falling, or undetectable viral load might suggest that it is.
Soon after starting treatment, a successful course of treatment induces a reduction in viral load of 99% or more, and after treatment is finished, the viral load is typically undetectable. An undetectable viral load in a treated person's blood 12 weeks after the completion of treatment indicates that the HCV infection has responded to therapy, per recommendations from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Disease Society of America.
Most Common Questions About the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test:
Clinical Utility and Interpretation
What is the main objective of the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test?
The Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test is primarily used to measure the amount (or load) of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA in the blood. This can give insights into the severity of a patient's hepatitis C infection and provide valuable information for treatment decisions.
How can the results of the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test affect treatment options?
Results from the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test can guide antiviral therapy choices and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. A decrease in HCV RNA levels typically indicates a positive response to therapy, while stable or increasing levels may suggest resistance or treatment failure.
Clinical Applications and Diagnoses
Why might a healthcare provider order the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test after confirming a hepatitis C diagnosis?
Once a hepatitis C diagnosis is confirmed using an antibody test, the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test is often ordered to determine the viral load. This helps gauge the severity of the infection and assists in determining the most suitable treatment regimen.
How often is the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test repeated during hepatitis C treatment?
The frequency depends on the specific treatment protocol and the patient's response. However, it's commonly repeated at various intervals to monitor treatment efficacy. Significant drops in viral RNA levels can indicate a favorable response.
Comparative Insights
How does the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test differ from the Hepatitis C antibody test?
The Hepatitis C antibody test detects the presence of antibodies against the hepatitis C virus, indicating exposure. In contrast, the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test measures the amount of the virus in the blood, offering a direct measure of the viral load and the activity of the infection.
Understanding Limitations and Challenges
Is it possible to have a positive Hepatitis C antibody test but a negative Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR result?
Yes, this can happen if a person was exposed to the virus in the past and developed antibodies, but the virus was cleared from their body either naturally or through treatment. The antibody test will be positive since antibodies remain, but the PCR test will not detect any active virus.
What does an "undetectable" result mean in the context of the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test?
An "undetectable" result means that the amount of HCV RNA in the blood is below the threshold that the test can measure. While this is a positive indicator and often a goal of treatment, it does not necessarily mean the virus has been completely eradicated from the body.
Additional Questions and Insights
How do different genotypes of the hepatitis C virus impact the results of the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test?
Different HCV genotypes don't typically affect the accuracy or interpretation of the viral load result itself. However, the genotype can influence treatment decisions and response rates, as some genotypes are more resistant to certain treatments than others.
Can the Hepatitis C Viral RNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR test determine the specific genotype of the hepatitis C virus?
No, the test is designed to quantify the amount of virus, not to determine its genotype. Separate genotyping tests are available to identify the specific HCV genotype, which can guide treatment decisions.
We advise having your results reviewed by a licensed medical healthcare professional for proper interpretation of your results.
